+86-13732282311
merlin@xcellentcomposites.com
Deixe o mundo se beneficiar de materiais compostos!
Ceramic Insulation Sheets: A Comprehensive Guide
Ceramic insulation sheets are an essential component in various industries that require efficient thermal insulation solutions. These sheets are widely used in applications ranging from industrial furnaces to automotive and aerospace sectors due to their high-temperature resistance, low thermal conductivity, and excellent durability.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore every aspect of ceramic insulation sheets, including their composition, manufacturing process, key properties, applications, benefits, selection criteria, installation methods, maintenance, environmental considerations, and future trends.

What Are Ceramic Insulation Sheets?
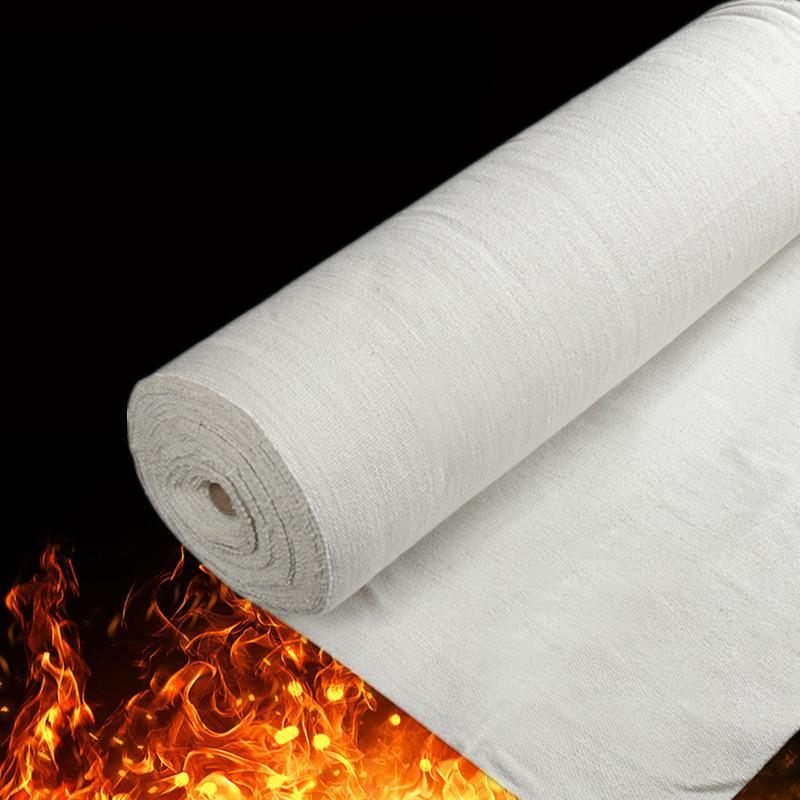
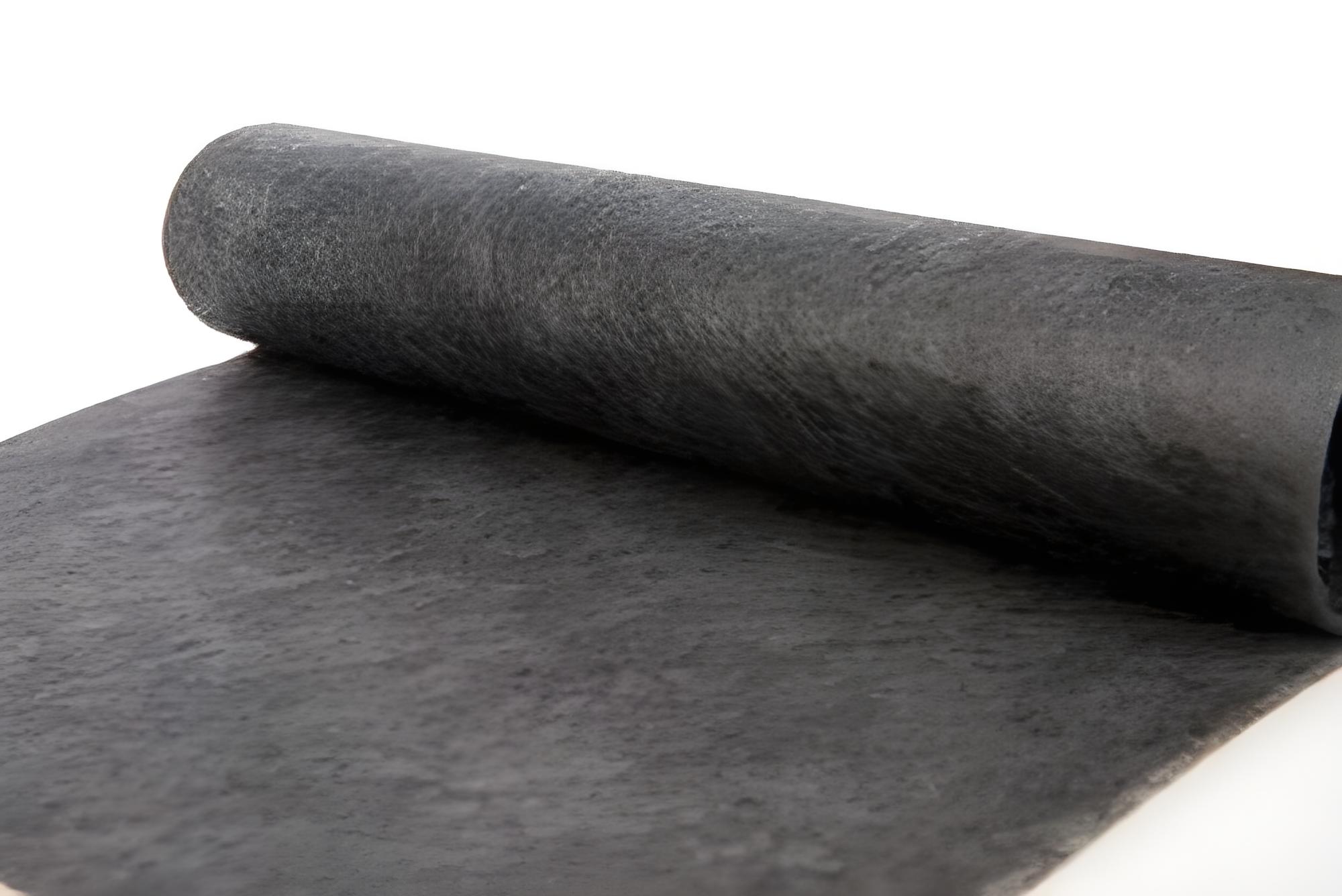
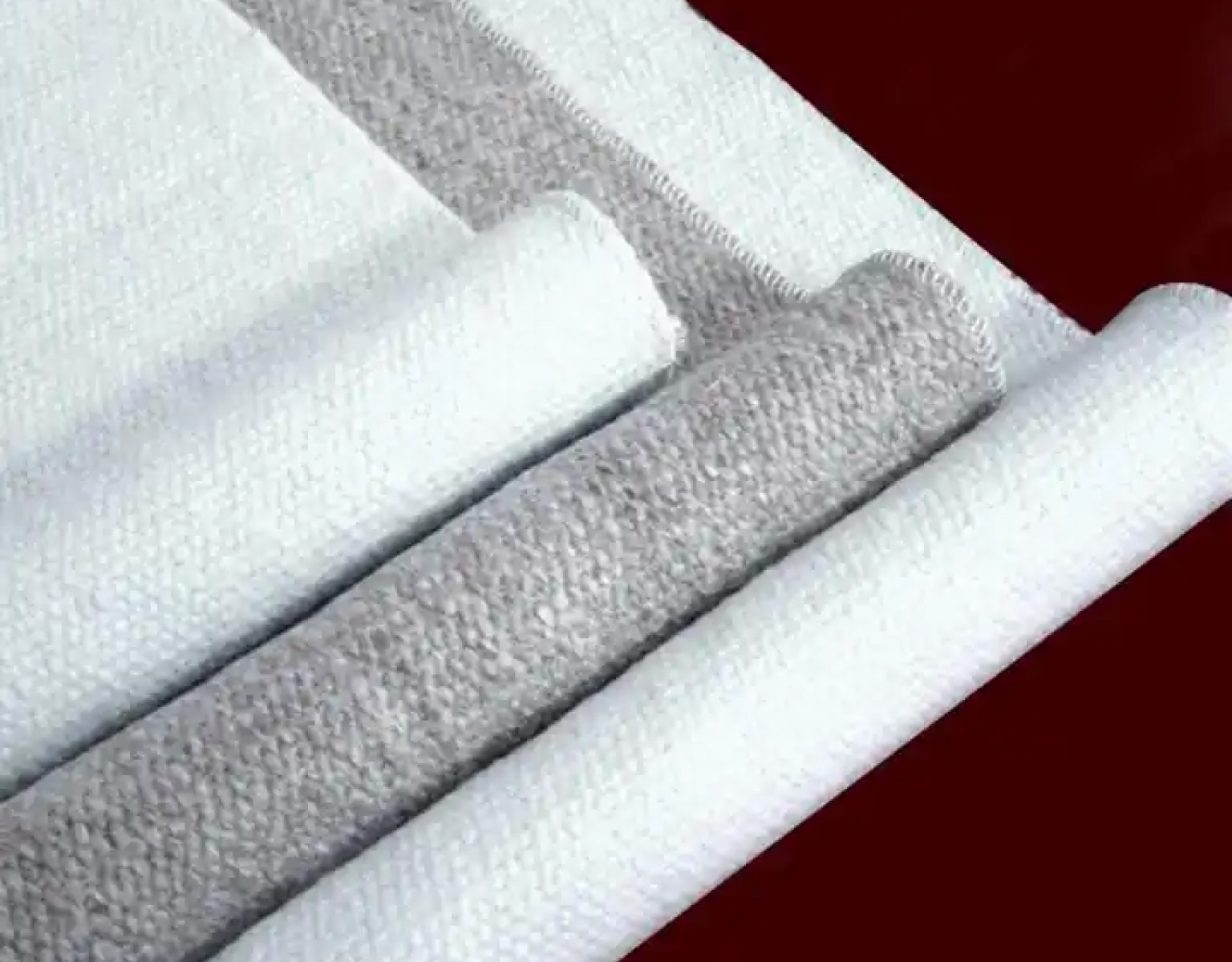
Ceramic insulation sheets, sometimes called ceramic fiber boards, are rigid, high-temperature-resistant materials composed of alumina (Al₂O₃) and silica (SiO₂) fibers. These sheets are engineered to provide superior thermal insulation in extreme conditions, making them ideal for industries where heat management is crucial.
Unlike conventional insulation materials like fiberglass, ceramic insulation sheets maintain their integrity even at extremely high temperatures, offering a reliable solution for thermal protection.
Manufacturing Process of Ceramic Insulation Sheets
The production of ceramic insulation sheets involves a specialized process to ensure uniform density, strength, and insulation properties. The main steps include:
1. Fiber Preparation
The first step involves the creation of high-purity ceramic fibers.
Alumina and silica materials are melted at high temperatures and then fiberized using advanced techniques like spinning or blowing.
2. Slurry Formation
The ceramic fibers are mixed with binders, such as organic or inorganic adhesives, and water to create a thick slurry.
This slurry ensures that the fibers are evenly distributed throughout the sheet.
3. Forming Process
The slurry is cast into molds or onto formers to create sheets of the desired thickness and size.
The forming stage determines the uniformity and strength of the final product.
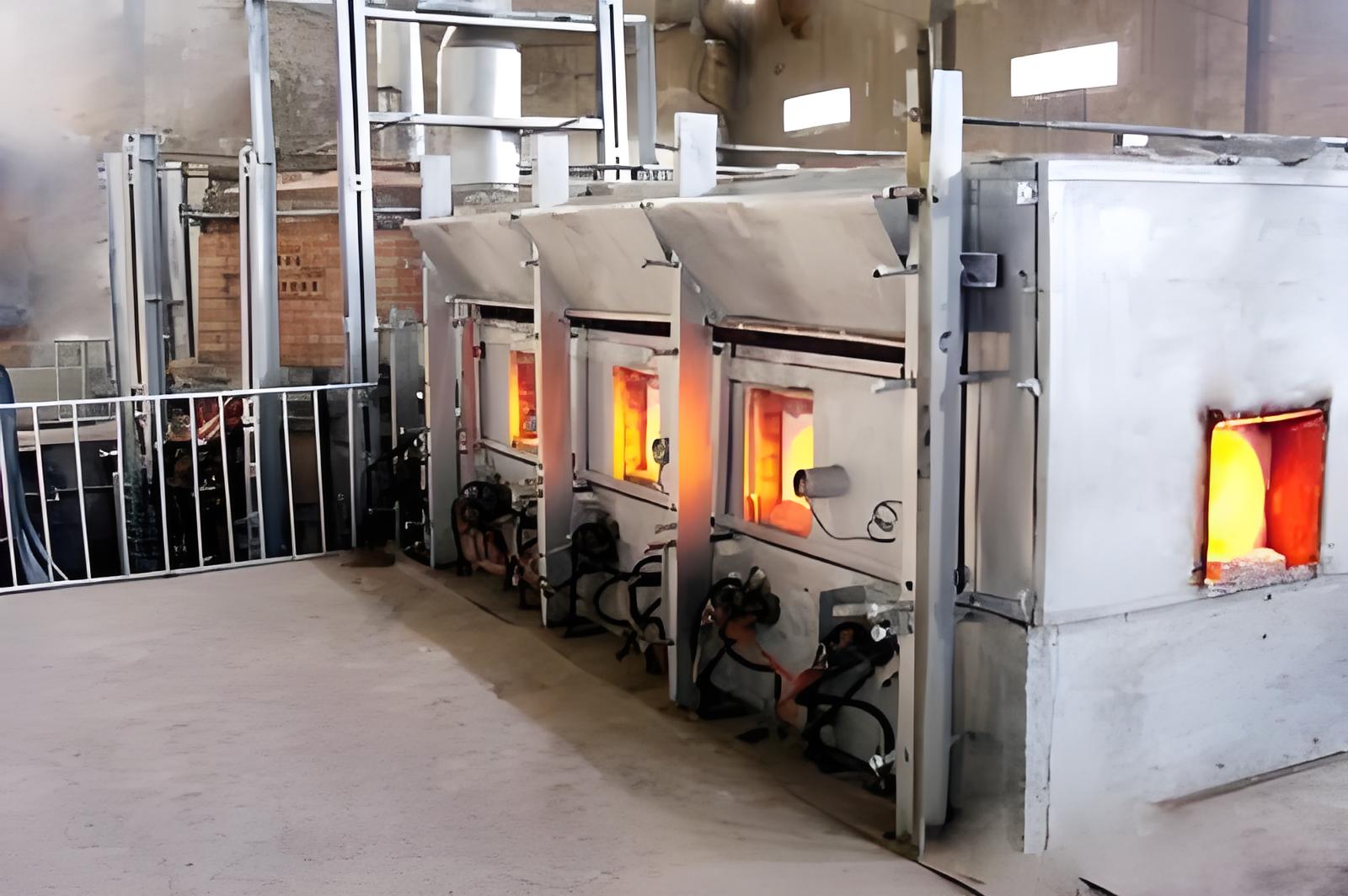
4. Drying and Firing
The formed sheets are dried to remove excess moisture.
They are then subjected to high temperatures in a furnace to enhance their mechanical strength and eliminate volatile components.
5. Finishing and Cutting
The sheets are trimmed, cut, and machined to meet specific industrial requirements.
Surface coatings may also be applied to enhance durability and resistance to environmental factors.
Key Properties of Ceramic Insulation Sheets
Ceramic insulation sheets are valued for their unique combination of properties:
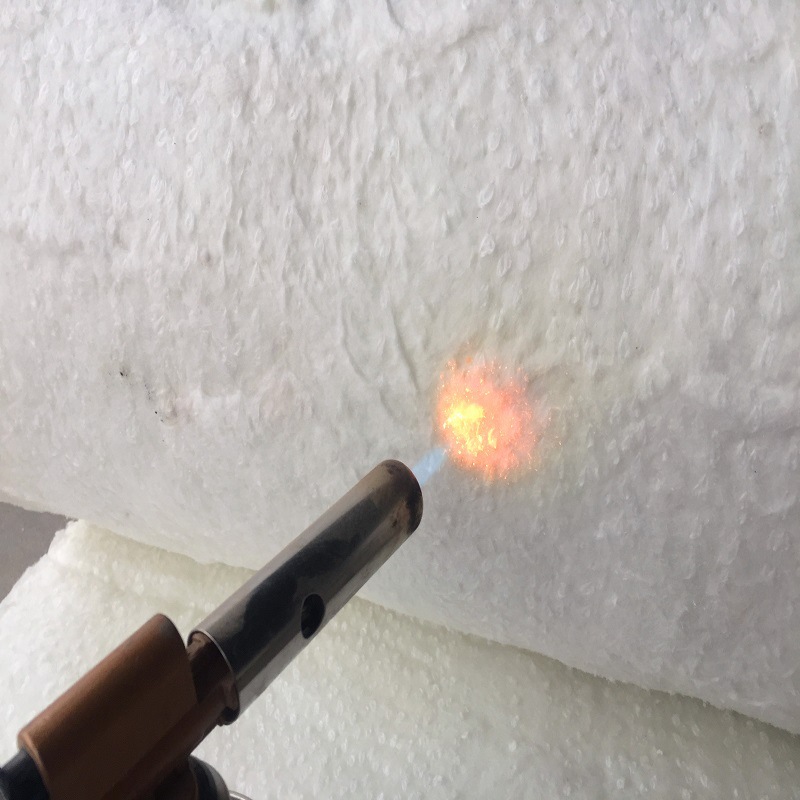
1. High-Temperature Resistance
Can withstand temperatures ranging from 1000°C to 1430°C (1832°F to 2600°F), depending on the material composition.
2. Low Thermal Conductivity
Provides excellent insulation, reducing heat loss and improving energy efficiency.
3. Chemical Stability
Resistant to most chemicals, including acids and alkalis.
Ensures longevity even in harsh environments.
4. Mechanical Strength
Offers good compressive and flexural strength.
Can withstand mechanical stress and high-pressure environments.
5. Low Density and Lightweight
Easy to handle and install due to its lightweight nature.
6. Thermal Shock Resistance
Can endure rapid temperature fluctuations without cracking or degrading.
7. Electrical Insulation
Some ceramic insulation sheets provide electrical insulating properties, making them suitable for applications involving electrical equipment.
Applications of Ceramic Insulation Sheets
Due to their outstanding properties, ceramic insulation sheets are used in a variety of industries and applications:
1. Industrial Furnaces and Kilns
Used as linings in high-temperature furnaces, kilns, and ovens.
Prevents heat loss and enhances energy efficiency in manufacturing plants.
2. Petrochemical Industry
Utilized in reformers, pyrolysis furnaces, and reactors.
Helps maintain optimal operating temperatures while preventing heat damage to surrounding structures.
3. Power Generation
Used in boilers, turbines, and high-temperature ducts.
Helps improve the efficiency of power plants by minimizing heat losses.
4. Fire Protection Systems
Installed in fire doors, firewalls, and other fire-resistant structures.
Provides a thermal barrier to slow down the spread of fires.
5. Glass and Ceramic Manufacturing
Used in annealing lehrs, tempering furnaces, and backup insulation layers.
Protects equipment and enhances process efficiency.
6. Automotive and Aerospace Sectors
Integrated into exhaust systems, catalytic converters, and heat shields.
Provides insulation for components exposed to extreme heat.
7. Metallurgical Applications
Found in foundries and metal-processing plants.
Helps maintain high-temperature conditions necessary for metal refining and casting.
A ceramic fiber insulation board offers excellent thermal resistance and durability, making it a reliable choice for high-temperature applications such as industrial furnaces and kilns.
Advantages of Ceramic Insulation Sheets
Using ceramic insulation sheets provides several benefits across different industries:
1. Energy Efficiency
Reduces heat loss, leading to lower energy consumption and cost savings.
2. Enhanced Safety
Minimizes the risk of heat-related injuries in workplaces.
Acts as a fire-resistant barrier.
3. Durability and Longevity
Withstands harsh environments and long-term exposure to extreme temperatures.
4. Design Flexibility
Can be customized in various shapes and sizes for specific applications.
5. Environmental Benefits
Some versions are made with eco-friendly, bio-soluble fibers that reduce environmental impact.
Selection Criteria for Ceramic Insulation Sheets
When choosing the right ceramic insulation sheet for your application, consider the following factors:
1. Maximum Operating Temperature
Select a sheet with a temperature rating that exceeds your application’s maximum temperature.
2. Density
Higher-density sheets offer better mechanical strength but may have slightly higher thermal conductivity.
3. Chemical Resistance
Consider the chemical environment where the sheet will be used.
4. Mechanical Load Requirements
Ensure the sheet has adequate compressive and flexural strength for structural support.
5. Ease of Installation
Consider factors like ease of cutting, handling, and fixing methods.
Installation Guidelines for Ceramic Insulation Sheets
Proper installation ensures the best performance and longevity:
1. Surface Preparation
Clean and dry the surface before installation.
Remove any dust, grease, or contaminants.
2. Cutting and Shaping
Use appropriate cutting tools, such as saws or water jets, to achieve precise dimensions.
3. Fixing Methods
Sheets can be installed using:
- Mechanical anchors
- Adhesive bonding
- Clamping systems
4. Sealing and Joint Treatment
Gaps between sheets should be sealed with refractory adhesives to prevent heat leaks.
Maintenance and Inspection
To ensure longevity and optimal performance, regular maintenance is necessary:
1. Routine Inspections
Check for cracks, wear, or signs of thermal degradation.
2. Cleaning
Remove dust and debris to prevent contamination.
3. Repair and Replacement
Damaged sheets should be replaced or repaired immediately.
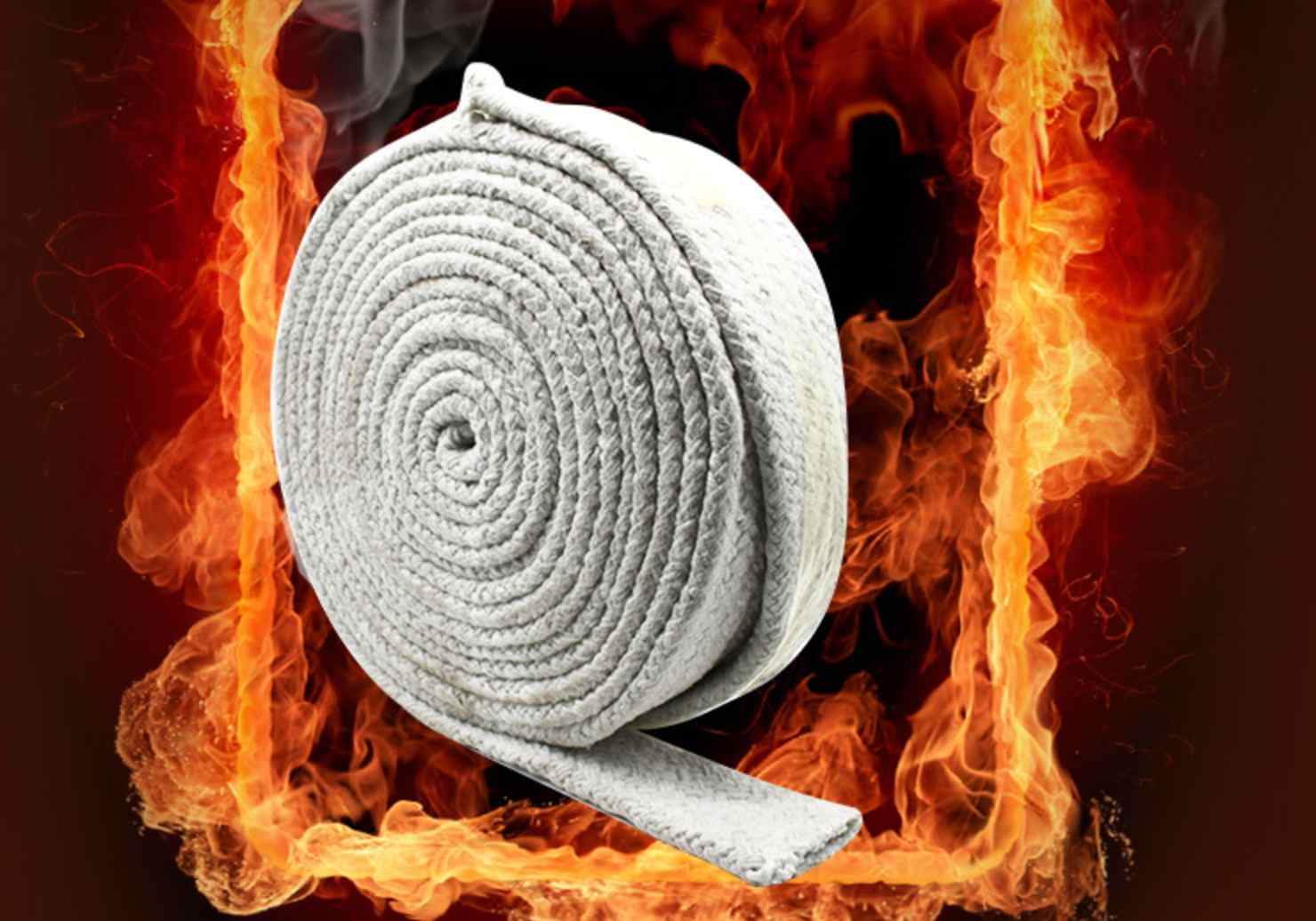

Environmental and Safety Considerations
Many modern ceramic insulation sheets are designed with sustainability and safety in mind:
1. Bio-Soluble Fibers
Some sheets use bio-soluble fibers to reduce health risks associated with inhalation.
2. Asbestos-Free Materials
Modern products do not contain asbestos, eliminating associated health hazards.
3. Proper Disposal Methods
Follow local environmental regulations for disposal to minimize impact.
Innovations and Future Trends in Ceramic Insulation
The field of ceramic insulation is evolving with advancements in material science:
1. Nanotechnology
Researchers are incorporating nanomaterials to enhance insulation efficiency and mechanical strength.
2. Hybrid Materials
New composites combine ceramic fibers with other insulating materials for improved performance.
3. Sustainable Manufacturing
The industry is moving towards more environmentally friendly production processes and recyclable materials.
Conclusion
Ceramic insulation sheets are indispensable for high-temperature applications due to their exceptional insulation properties, durability, and energy efficiency. Whether used in industrial furnaces, power plants, or fire protection systems, these sheets play a crucial role in heat management.
By understanding their composition, properties, and applications, industries can select the right ceramic insulation sheets to enhance safety, reduce energy consumption, and improve operational efficiency.
Read More: Research Progress and Application of Polyimide Fiber
Materiais compostos populares
Materiais compostos populares
Compósitos Hub de conhecimento
Compósitos Hub de conhecimento